Diagnostic Workup
DIAGNOSTIC WORKUP
Reproductive Endocrinology
Reproductive endocrinology is a subspecialty of obstetrics and gynecology that focuses on the biological and hormonal aspects of human reproduction as well as the underlying issues affecting fertility. Reproductive endocrinologists, are trained to diagnose and treat a wide range of reproductive health issues including infertility, hormonal dysfunction, and conditions related to the menstrual cycle.
Their expertise encompasses both male and female reproductive systems, allowing them to address complex fertility problems with comprehensive treatment plans. Utilizing advanced diagnostic tests and assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), reproductive endocrinologists aim to help individuals and couples achieve successful pregnancies and address reproductive health concerns with precision and care.
MEET YOUR REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGIST
Dr. Chauhan
Dr. Subodh Chauhan, Founder and CEO of New Hope Fertility Institute of Texas, is Board Certified in Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Endocrinology. A Clinical Assistant Professor at Baylor College of Medicine, he has trained in India, the UK, and the USA.
Known for his personalized care, Dr. Chauhan performs IVF and Embryo transfers for all his patients and is highly regarded for his compassionate and ethical approach.


A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
What to Expect
A comprehensive reproductive endocrinology diagnostic workup is essential for identifying underlying fertility issues and developing an effective treatment plan. Here's what to expect during this thorough process:
Initial Consultation and Medical History
The first step involves an in-depth consultation with Dr. Chauhan. During this meeting, you'll discuss your detailed medical history, lifestyle factors, and any previous fertility treatments. This information helps him understand any potential issues and tailor the diagnostic process accordingly.
Physical Examination
A physical examination may be conducted to assess your overall health and identify any physical signs that could affect fertility. For women, this may include a pelvic exam to evaluate the reproductive organs.
Hormonal Testing
Blood tests are an integral part of the diagnostic workup. These tests measure hormone levels, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estrogen, progesterone, and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH). These hormones provide insights into ovarian reserve, ovulation status, and overall reproductive health.
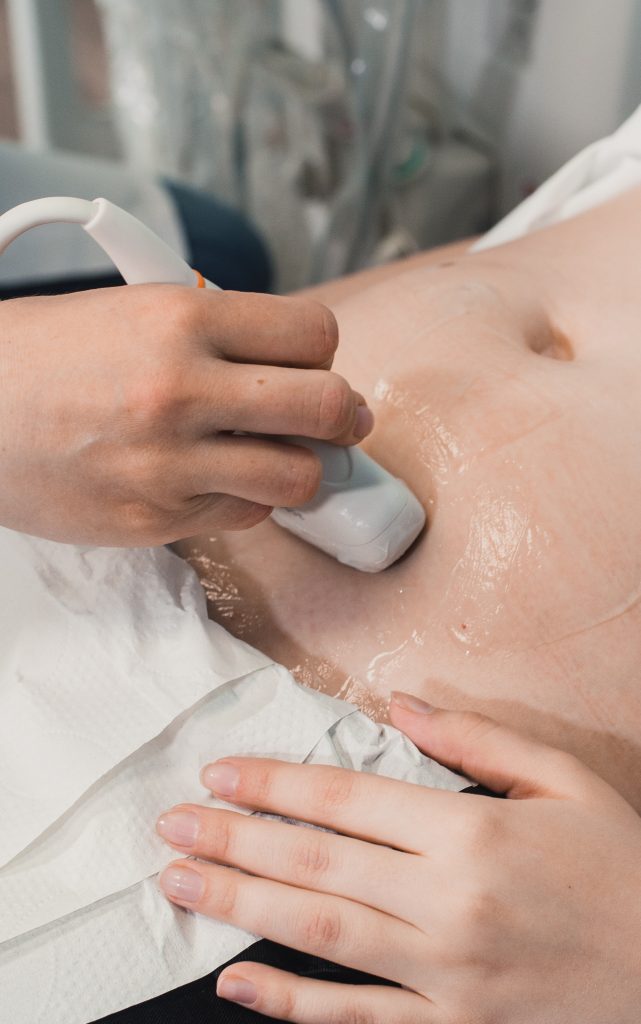
Ultrasound Examination
Transvaginal ultrasound is used to visualize the ovaries, uterus, and antral follicles. This imaging technique helps assess ovarian function, detect structural abnormalities, and monitor follicle development throughout the menstrual cycle.
Semen Analysis
For male partners, a semen analysis is performed to evaluate sperm count, motility, and morphology. This test is crucial for identifying male factor infertility and planning appropriate interventions.
Specialized Testing
Depending on individual circumstances, additional specialized tests may be recommended. These could include hysterosalpingography (HSG) to check for blockages in the fallopian tubes, laparoscopy to look for endometriosis or pelvic adhesions, and genetic testing to identify chromosomal anomalies.
Review and Treatment Planning
Once all diagnostic tests are completed, Dr. Cahuhan will review the results and discuss them with you in detail. Based on the findings, a personalized treatment plan is formulated to address the identified issues and improve the likelihood of achieving a successful pregnancy.
By undergoing this comprehensive diagnostic workup, patients can gain a clear understanding of their reproductive health and receive tailored treatments designed to maximize their chances of conception.


COMMON CAUSES
Infertility
Infertility can be attributed to various factors affecting either one or both partners. Understanding these causes is crucial for diagnosing and treating fertility issues effectively.
Here are some of the most common causes of infertility:
Ovulation disorders, which include conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can prevent the release of eggs from the ovaries. Without ovulation, fertilization cannot occur, making it a significant cause of infertility.
Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes can prevent sperm from reaching the egg or block the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus. This condition can be caused by pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, or previous surgeries.
Issues within the uterus or cervix, such as fibroids, polyps, or congenital abnormalities, can interfere with the implantation of the fertilized egg or increase the risk of miscarriage.
Male infertility can result from various issues including low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or abnormal sperm morphology. Factors such as genetic conditions, infections, and lifestyle choices can significantly impact sperm health.
Age-related infertility is a natural cause where the quality and quantity of a woman’s eggs decline as she ages. Similarly, male fertility can decrease with age, affecting sperm count and motility.
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside of it, causing inflammation and scarring that can obstruct the reproductive organs and impair fertility.
Various lifestyle choices, including excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise, can negatively affect fertility. Managing stress and maintaining a healthy weight are also important for optimizing reproductive health.
Certain genetic conditions can impact fertility by disrupting normal reproductive function. Both partners may be tested for genetic abnormalities if infertility is unexplained or if there’s a known family history.
In some cases, infertility remains unexplained despite thorough testing. This can be particularly challenging, but fertility treatments and assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can still offer hope for conception.
INFERTILITY
Diagnostic Testing
New Hope Fertility Institute utilizes a variety of diagnostic tests to evaluate fertility-related issues. Here are some of the most common tests:
Hormone testing typically involves blood tests to measure levels of hormones such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estradiol, progesterone, and thyroid hormones. These tests help assess ovarian reserve, ovulation status, and the overall hormonal environment.
A transvaginal ultrasound is an imaging test that uses a small probe inserted into the vagina to visualize the ovaries, uterus, and sometimes the fallopian tubes. It helps detect abnormalities such as ovarian cysts, fibroids, or polyps and assesses follicular development during the menstrual cycle.
HSG is a specialized X-ray procedure used to evaluate the shape of the uterine cavity and the patency of the fallopian tubes. It involves injecting a contrast dye into the uterine cavity, which can reveal blockages or structural abnormalities that may impact fertility.
Semen analysis is a fundamental test for assessing male fertility. It evaluates sperm count, motility, morphology, and overall semen quality. This test can identify issues such as low sperm count, poor motility, or abnormal sperm shape.
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows direct visualization of the pelvic organs. It can diagnose conditions like endometriosis, pelvic adhesions, and tubal obstructions. During the procedure, a thin, lighted tube called a laparoscope is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen.
Hysteroscopy is a procedure that uses a thin, flexible tube with a camera (hysteroscope) to examine the inside of the uterus. It helps diagnose and sometimes treat uterine abnormalities such as fibroids, polyps, and adhesions.
Genetic testing may be performed to identify chromosomal abnormalities or genetic mutations that could affect fertility or increase the risk of miscarriage. Both partners may undergo genetic screening to provide a comprehensive view of potential genetic factors.
Ovarian reserve testing assesses the quantity and quality of a woman’s remaining eggs. Tests may include antral follicle count (AFC) via ultrasound and blood tests measuring anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels.

REAL PATIENTS, REAL SUCCESS
Patient Testimonials
DIAGNOSTIC WORKUP
FAQs
During your initial consultation, you will have an in-depth discussion with Dr. Chauhan about your medical history, lifestyle factors, and any previous fertility treatments. This information helps tailor the diagnostic process to your specific needs.
The duration of the diagnostic workup can vary, but it generally takes a few weeks to complete all necessary tests and reviews. Dr. Chauhan will provide a more specific timeline based on your individual situation.
Not all tests may be necessary for everyone. Dr. Chauhan will recommend tests based on your initial consultation and medical history. Some patients may only need a few tests, while others might require a comprehensive assessment.
Most of the tests involved in the diagnostic workup are non-invasive and carry minimal risks. However, certain procedures like laparoscopy or hysterosalpingography (HSG) may have some risks which will be explained to you in detail by Dr. Chauhan before proceeding.
Yes, partner involvement is crucial, especially for tests like semen analysis. Dr. Chauhan will discuss the importance of both partners undergoing evaluation to get a comprehensive understanding of your fertility.
Even if test results are normal, there might still be underlying issues such as unexplained infertility. Dr. Chauhan will discuss potential treatment options, which can include lifestyle changes, medication, or assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Once all diagnostic tests are completed and the results reviewed, Dr. Chauhan will discuss the findings with you and formulate a personalized treatment plan. Treatment can typically begin shortly after the review and discussion, depending on your specific needs and preferences.




NEW HOPE FERTILITY
Insurance
At New Hope Fertility Institute of Texas, we understand the financial stress that infertility treatments can impose. We are committed to making advanced fertility care accessible to as many patients as possible. That's why we are pleased to announce that we accept most insurance plans.
Our knowledgeable staff will work closely with you to help navigate your insurance benefits and ensure you receive the maximum coverage possible for your IVF treatment. We encourage you to contact our office for specific details about your insurance plan and the extent of your coverage.
EDUCATIONAL RESOURCE
Follow Our YouTube
Stay informed and inspired by subscribing to our YouTube channel! Follow us for the latest updates and valuable insights on navigating your fertility journey.
GET IN TOUCH
Start Your Journey
If you are considering treatment and would like to learn more about how New Hope Fertility Institute of Texas can support you on your journey to parenthood, we invite you to reach out to us. Our dedicated team is here to answer any questions you may have and provide personalized guidance tailored to your unique circumstances.



NEW HOPE FERTILITY
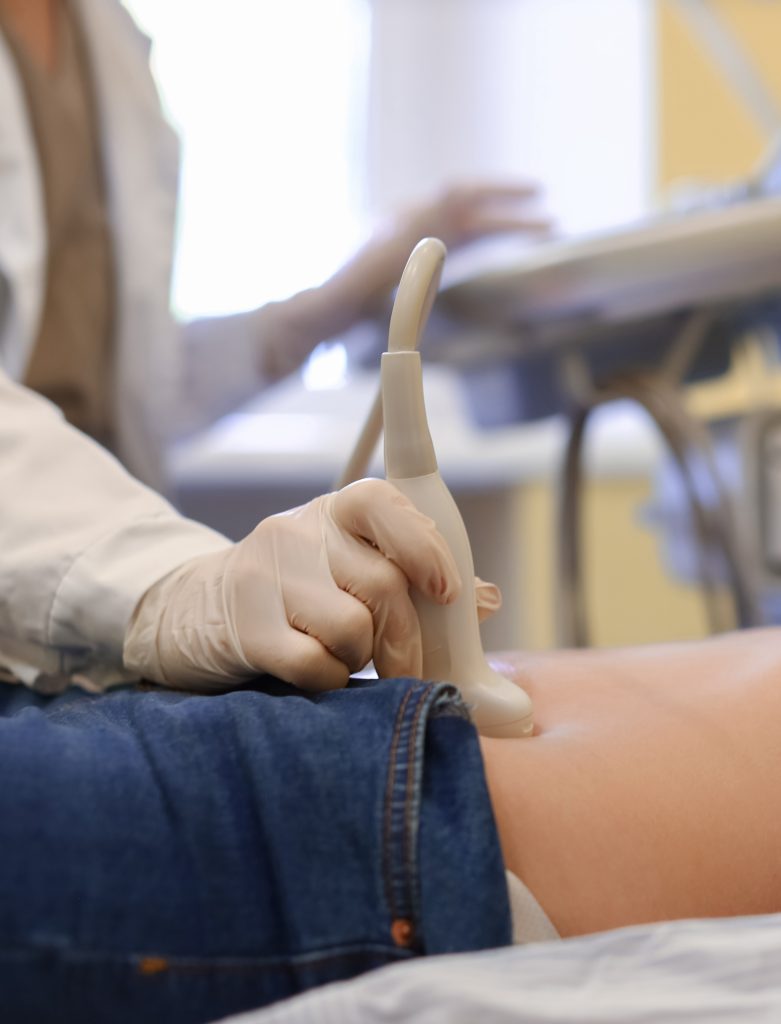
Free
Ovarian Reserve
Testing
Ultrasound, AMH, FSH, LH and Inhibin testing.
Email info@newhopefitx.com to schedule.

