Egg Donation
A PATH TO PARENTHOOD
What Is Egg Donation?
At New Hope Fertility Institute of Texas, we understand that the journey to parenthood can take many different paths. For individuals or couples facing challenges with their own egg production, donor eggs offer a remarkable opportunity to achieve a successful pregnancy and build the family they've always dreamed of.
Whether you are a potential recipient seeking to start or expand your family, or someone considering the generous act of donating eggs, you will find comprehensive resources and compassionate care every step of the way.
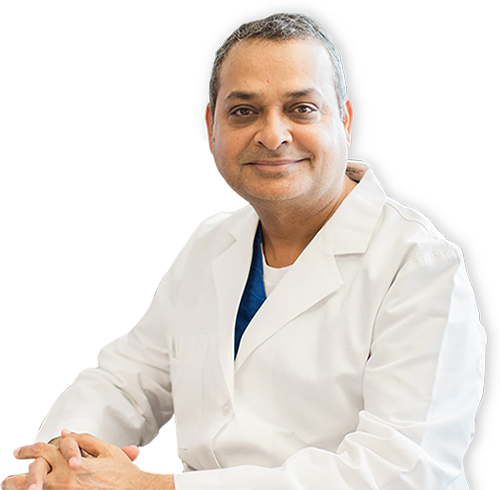
MEET YOUR REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGIST
Dr. Chauhan
Dr. Subodh Chauhan, Founder and CEO of New Hope Fertility Institute of Texas, is Board Certified in Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Endocrinology. A Clinical Assistant Professor at Baylor College of Medicine, he has trained in India, the UK, and the USA.
Known for his personalized care, Dr. Chauhan performs IVF and Embryo transfers for all his patients and is highly regarded for his compassionate and ethical approach.


A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
The Egg Donation Process
1. Initial Consultation & Screening:
Potential egg donors undergo a thorough medical and psychological evaluation to ensure they are suitable candidates. This includes medical history reviews, physical exams, blood tests, and psychological assessments. The screening process is essential to confirm that donors are in good health and do not carry any genetic disorders.
2. Legal & Ethical Considerations:
Prior to proceeding, donors and recipients both receive counselling regarding the legal and ethical aspects of egg donation. This ensures that all parties fully understand their rights and responsibilities. Legal agreements are then signed to outline the terms and protect the interests of both the donor and the recipient.
3. Ovarian Stimulation
Once approved, the donor begins a course of hormone injections designed to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. This process is monitored closely through blood tests and ultrasound scans to track the development of the follicles and adjust medication dosages as needed.
4. Egg Retrieval
When the eggs are mature, a minor surgical procedure known as follicular aspiration is performed to retrieve them. This is usually done under light sedation or anesthesia. Using an ultrasound-guided needle, a fertility specialist collects the eggs from the ovaries. The procedure typically takes about 20-30 minutes, and donors can usually return home the same day.
5. Fertilization and Embryo Development
The retrieved eggs are then fertilized with sperm in a laboratory setting to create embryos. These embryos are monitored and allowed to develop for a few days. The best-quality embryos are selected for transfer or may be frozen for future use.
6. Embryo Transfer
In the case of a fresh embryo transfer, one or more embryos are transferred to the recipient's uterus within a few days of fertilization. Alternatively, if the embryos are frozen, the transfer can occur at a later date that suits the recipient's schedule and health.


DONOR EGGS
Fresh Eggs
Fresh donor eggs refer to eggs that are retrieved from a donor and fertilized almost immediately. This approach maximizes the viability of the eggs and often results in higher success rates for implantation and pregnancy. With fresh eggs, the synchronization between the donor and the recipient's cycles ensures optimal timing for both fertilization and embryo transfer. The use of fresh donor eggs also allows for the possibility of creating additional embryos for future transfer, offering a greater chance of success in subsequent cycles.
The main benefits of choosing fresh donor eggs include:
Fresh eggs typically have higher fertilization and pregnancy rates compared to frozen eggs, as they have not undergone the freezing and thawing process, which can sometimes affect their quality.
Fresh eggs are considered to have a better overall viability, reducing the risk of potential damage during storage or thawing processes.
With a fresh egg cycle, there is more control over the timing of the donor’s egg retrieval and the recipient’s preparation for embryo transfer, allowing a more tailored approach to treatment.
DONOR EGGS
Frozen Eggs
Frozen donor eggs provide an alternative that can offer greater flexibility and convenience for some recipients. These eggs have been retrieved, frozen, and stored at an earlier date, making them readily available for use without the need to synchronize cycles. While frozen eggs can be a viable option, they do sometimes present challenges, such as the potential for lower success rates due to the freezing and thawing process.


REAL PATIENTS, REAL SUCCESS
Patient Testimonials
DONOR EGGS
FAQs
Egg donation is a process where a woman donates her eggs to help another individual or couple conceive a child. These eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory to create embryos, which are then transferred to the recipient’s uterus.
Egg donors are typically healthy women between the ages of 21 and 32 who have a good medical history and no genetic disorders. They must also pass a thorough medical and psychological screening process.
While the process includes hormonal injections and a minor surgical procedure to retrieve the eggs, most donors experience only mild discomfort. The egg retrieval is performed under sedation or anesthesia to minimize pain.
The entire process, from initial screening to egg retrieval, typically takes about 4 to 6 weeks. This includes the time needed for medical evaluations, ovarian stimulation, and monitoring.
Yes, egg donors are financially compensated for their time, effort, and commitment.
Egg donation does not typically affect a woman’s future fertility. The hormone medications used stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, some of which would naturally go unused in a typical menstrual cycle.
While generally safe, egg donation carries some risks including Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS), bleeding, infection, and potential reactions to anesthesia. These risks are rare and medical professionals take steps to minimize them.
Most egg donation programs are anonymous, meaning the donor and recipient do not know each other’s identities. However, some programs allow for semi-anonymous or known donations, depending on the preferences and legal stipulations.
Guidelines usually recommend that a woman donates eggs no more than six times. This recommendation is based on both ethical considerations and medical guidelines to protect the donor’s health.




NEW HOPE FERTILITY
Insurance
At New Hope Fertility Institute of Texas, we understand the financial stress that infertility treatments can impose. We are committed to making advanced fertility care accessible to as many patients as possible. That's why we are pleased to announce that we accept most insurance plans.
Our knowledgeable staff will work closely with you to help navigate your insurance benefits and ensure you receive the maximum coverage possible for your IVF treatment. We encourage you to contact our office for specific details about your insurance plan and the extent of your coverage.
EDUCATIONAL RESOURCE
Follow Our YouTube
Stay informed and inspired by subscribing to our YouTube channel! Follow us for the latest updates and valuable insights on navigating your fertility journey.
GET IN TOUCH
Start Your Journey
If you are considering Egg Donation and would like to learn more about how New Hope Fertility Institute of Texas can support you on your journey to parenthood, we invite you to reach out to us. Our dedicated team is here to answer any questions you may have and provide personalized guidance tailored to your unique circumstances.



NEW HOPE FERTILITY
Free
Ovarian Reserve
Testing
Ultrasound, AMH, FSH, LH and Inhibin testing.
Email info@newhopefitx.com to schedule.

